
6 myths about gum health you should know
Actor portrayal
More than 65 million people in the U.S. suffer from gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, a chronic bacterial infection that damages soft tissue.
Without treatment, it can destroy the gums and bone that support your teeth. Despite its significant prevalence, there are many misconceptions about risk factors, symptoms of the infection, and how to best treat it. Some at-risk individuals may be misled about the truth behind gum disease as false claims about prevention and "cures" are widespread across the internet and social media.
Here are six common myths and facts about gum health that you should know.
Bleeding gums are normal
FACT: Gums that bleed while brushing or flossing may indicate an infection, and they can be an early warning sign of gum disease. Other key signs include red or swollen gums and bad breath that doesn't go away after brushing. If these signs arise, you should contact a dental care provider immediately. If left untreated, the gums can pull away from the teeth, creating pockets of bacteria that can spread to the roots of the teeth. Over time, as pockets worsen and bacteria spreads, the gums and bone can become permanently damaged, causing teeth to loosen or require removal.
Only oral health is impacted by gum disease
FACT: Gum disease can have systemic effects on the body and has been linked to various health conditions such as cardiovascular disease. That's one of many reasons why good oral hygiene and regular dentist visits are so critical.
Just older people get gum disease
FACT: Gum disease can affect anyone. Nearly half of all U.S. adults aged 30 years and older have gum disease. While the risk increases with age, other factors, including oral hygiene habits, smoking, and genetic predisposition can affect your risk of developing gum disease earlier in life. Therefore, anyone can be at risk for developing it, regardless of age.
Brushing and flossing are the best way to treat gum disease
FACT: While brushing and flossing your teeth are part of good oral hygiene and important steps to help prevent the onset of gum disease, they cannot heal your gums once an infection takes hold. In conjunction with good oral hygiene, reoccurring dental visits to evaluate your current gum health and administer ongoing treatment are the only way to prevent further damage.
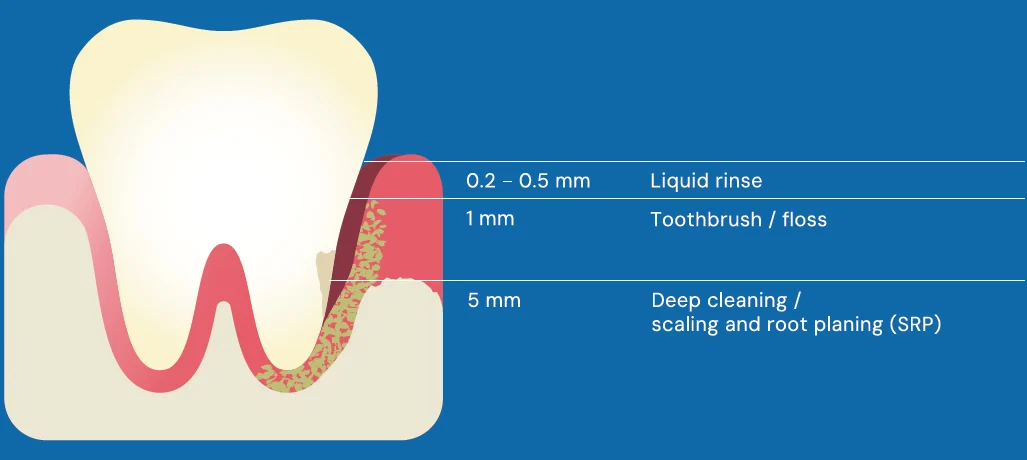
How far brushing and flossing truly reaches
Gum disease is a result of poor oral hygiene
FACT: Gum disease is your body's reaction to infection, and it can have a variety of causes, including genetic predisposition and lifestyle factors like smoking or chewing tobacco. Oral hygiene, while a vital step in preventing gum disease, is not the only cause.
Gum disease is curable
FACT: Gum disease cannot be cured, only managed through ongoing treatment. It is a chronic, lifelong infection that may require more frequent dental visits. If you think you might be at risk for gum disease, talk to your dental care provider about your treatment options.
An Option to Treat Gum Disease Comprehensively
There are a variety of treatment options available for gum disease patients. One option is ARESTIN (minocycline HCI) Microspheres, 1 mg, an antibiotic used in combination with SRP to fight the bacteria at the site of infection.
What is ARESTIN?
ARESTIN is used in combination with scaling and root planing (SRP) procedures to treat patients with adult periodontitis (gum disease). ARESTIN may be used as part of an overall oral health program that includes good brushing and flossing habits and SRP.
Don't take ARESTIN if you are allergic to minocycline or tetracyclines. Ask your dentist or pharmacist for a list of these drugs if you are not sure. ARESTIN should not be used in children or in pregnant or nursing women because ARESTIN, like other tetracycline medicines may cause permanent discoloration of the teeth during tooth development.
How ARESTIN Works
ARESTIN enhances the effects of SRP by penetrating the gums. It starts as a fine powder and fills the pocket to fight bacteria. SRP is effective, but it has some limitations. It cannot always reach the base of deeper gum pockets where bacteria may remain.
During treatment, a dental care provider will apply ARESTIN directly to the infected gum pockets after SRP has been performed. A dental care provider may apply ARESTIN during the same visit as the SRP or during a follow-up visit. Treatment does not require any needles or anesthesia.
In a clinical trial, in combination with SRP, ARESTIN provided 20% more reduction of pocket depth at 9 months.*
The most common adverse events reported by ≥ 3% of patients in the ARESTIN group include: dental pain, swollen gums, headache, mouth ulcers, flu like symptoms, sore throat, pain, stomach upset, and mucous membrane disorder.
STUDY DESIGN AND RESULTS*
SRP + vehicle, and (3) SRP + ARESTIN. Retreatment occurred at 3 and 6 months after initial treatment, and any new site with pocket depth ≥5 mm also received treatment. Patients treated with ARESTIN were found to have statistically significantly reduced probing pocket depth compared with those treated with SRP alone or SRP + vehicle at 9 months after initial treatment. ARESTIN vs SRP alone (n=250) p<0.01; ARESTIN vs vehicle + SRP (n=249) p<0.001; ARESTIN + SRP vs vehicle (n=249) p<0.001.
Speak to your dental care provider about gum disease and ask if ARESTIN is the right option for you.
Please see Important Safety Information and full Prescribing Information
References:
Smile Generation, American Diabetes Association. (n.d.). Diabetes and gum disease: A two-way street. Diabetes and Gum Disease Risk | ADA. https://diabetes.org/about-diabetes/complications/oral-gum-disease#:~:text=If%20you%20develop%20gum%20disease,against%20gum%20disease%20and%20inflammation
Questions?
We’re here to help.
Contact our Customer Care team at 1-866-273-7846.
Contact our Customer Care team at 1-866-273-7846.
Monday - Friday, 8:30 am - 5:00 pm ET
You’re encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visit www.fda.gov/medwatch or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
You’re encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visit www.fda.gov/medwatch or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
What is ARESTIN?
What is ARESTIN?
ARESTIN® (minocycline HCl) Microspheres, 1mg is used in combination with scaling and root planing (SRP) procedures to treat patients with adult periodontitis (gum disease). ARESTIN® may be used as part of an overall oral health program that includes good brushing and flossing habits and SRP.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
- Do not use ARESTIN if you are allergic to minocycline or tetracyclines, ask your dentist if you are not sure. Do not use ARESTIN in children, pregnant or nursing women as the use of tetracycline class drugs, including ARESTIN, during tooth development may cause permanent discoloration of the teeth.
- ARESTIN may cause you to be sensitive to sunlight. Patients exposed to direct sunlight or ultraviolet light may develop a severe sunburn. At the first evidence of skin redness, call your dentist.
- Serious allergic reactions have occurred with oral minocycline. Get emergency help right away if you experience any signs of an allergic reaction including shortness of breath, swelling of the face, throat and tongue, rash, hives, itching, fever, or enlarged lymph nodes.
- Tetracyclines, including oral minocycline, have been associated with the development of autoimmune syndromes with symptoms such as joint pain, muscle pain, rash, swelling, fever, enlarged lymph nodes, and general body weakness.
- Tell your dentist about all the medicines you take, and about any health problems you have, including if you’ve had oral candidiasis (“thrush”).
- ARESTIN has not been studied in patients with weakened immune systems, such as patients with HIV infections or diabetes, or those receiving chemotherapy or radiation.
- The most frequently reported non-dental side effects were headache, infection, flu symptoms, and pain.
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visit www.fda.gov/medwatch or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visit www.fda.gov/medwatch or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
Please see full Prescribing Information here
What is ARESTIN?
ARESTIN® (minocycline HCl) Microspheres, 1mg is used in combination with scaling and root planing (SRP) procedures to treat patients with adult periodontitis (gum disease). ARESTIN® may be used as part of an overall oral health program that includes good brushing and flossing habits and SRP.


